Lumbar canal stenosis with neurological claudication
LCS is the narrowing of spinal canal, through which spinal cord and nerves traverse. The space around spinal cord becomes narrow, so it compresses ongoing spinal cord and nerve, which produces pain and numbness in lower limbs.
Causes:
1. Disc herniation – Acute disc bulge when becomes chronic usually represents the symptoms of LCS.
2. Thickening of ligaments around spinal cord and vertebraes.
3. Lumbar spondylolisthesis – Listhesis / slipping of one vertebrae over the other also compresses the spinal cord.
4. Bony spurs- usually arthritic changes in the vertebrae, produces bony outgrowths, which may put a pressure on traversing nerves. Bony outgrowths in Paget’s disease is the classic example of this.
5. Tumors- rarely spinal cord tumors may compress spinal cord.

Symptoms :
1. Neurological claudication – The classical symptom of LCS is neurological claudication. It is the occurrence of radicular pain and numbness in lower limbs when a person walks, making it difficult to walk and it disappears as soon as the person sits down. It is due to increase in blood flow in the vessels surrounding spinal cord, which increases compressive forces on spinal cord. Thus, pain provokes when a person walks.

2. Radicular Pain – Pain in one or both lower limbs, usually starting from hips, covering thighs and calves and going to sole of the foot.
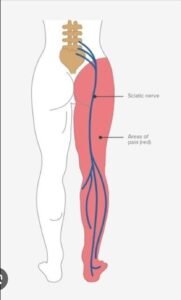
3. Tingling and numbness – Abnormal sensations like tingling – numbness is observed in foot and calf muscles. Sometimes, burning sensations are also associated with it.
Claudication distance – It is the distance through which neurological claudication appears that is the distance at which pain and numbness starts in leg as the person walks. It can vary from few steps to few meters. It is very important in marking the severity of LCS.
Diagnosis :
Physical examination along with thorough history taking and observations are helpful in making a probable diagnosis, however confirmatory tests are required to eliminate differential diagnosis.
1. MRI spine- It demonstrates any narrowing in canal by measuring the diameter of the spinal canal. Hence it is the confirmatory and most important test for LCS.2. CT Mylogram – CT scan shows a clearer picture of spinal cord and vertebraes, this accurately suggests LCS and its underlying cause.
LCS with neurological claudication, usually a chronic condition, affects daily activities extremely, specially it decreases walk range of an individual, when ignored may further increase de-formative forces on spinal cord hence it becomes important to start treating the disease as soon as possible.
